Blog Post No. 53
14th October 2017
Copyright © Renata Taylor-Byrne 2017
Renata’s Coaching Blog:
Do you want to feel better tomorrow morning, at no cost? The amazing power of sleep can transform your life
Introduction
This blog is a rave review of a book review I read, two weeks ago, in the Sunday Times Culture Magazine (October 1st 2017). It was written by James McConnachie.
He was reviewing ‘Why we sleep’- a book written by Matthew Walker, who is a professor of neuroscience and psychology at Berkeley, California. The book was published in September of this year.

Vital facts about sleep
McConnachie has done a very clear and fluent analysis of this book, ‘Why we sleep’, and has picked out some fascinating facts about why sleep is so important, and how we could all benefit from being more aware of its importance. In this blog post, I will present some of these gems so you can have the latest findings on sleep and how it makes you feel better. Of course, to gain the benefits, you would have to take on board the implications of the research findings. They really clarify, on the basis of sound research, the importance of sleep for our well-being.

A vital fact: We need a minimum of 8 hours sleep every night!
If you think you can get by on less than 8 hours sleep a night, then you are most likely wrong. According to Matthew Walker:
“You have forgotten what it is like to function properly”.
 Walker estimates that 2 out of 5 people in the UK are not having the sleep that they need, and he points out the consequences of not having enough sleep, which you may not be aware of. I will now present some of those consequences.
Walker estimates that 2 out of 5 people in the UK are not having the sleep that they need, and he points out the consequences of not having enough sleep, which you may not be aware of. I will now present some of those consequences.
What happens when we don’t get enough sleep?
Short sleepers eat an average of 300 calories extra per day, adding up to 10lb to 15lb of weight gain over a year! This is because people who don’t get enough sleep tend to eat more. (Their bodies produce more ghrelin, which is a hormone that makes you feel hungry. They also produce less leptin, which is the hormone that makes you feel full up). You also become vulnerable to some of those medical conditions which sleep protects us from. What are those conditions?

Sleep protects us from:
According to Walker’s research, sleep protects us from:
# Influenza
# Infections
# Dementia
# Heart disease; and:
# Mental ill health. (Walker states that: “There is no major psychiatric condition in which sleep is [found to be] normal”.)
Adequate sleep also protects us from car crashes. (Drowsiness, resulting from sleep deprivation or insufficiency causes more road accidents than drugs and alcohol combined).
Walker also states that adults of 45 and over, who sleep fewer than 6 hours a night, are 200% more likely to have a heart attack or stroke!
So what are the benefits of adequate sleep, apart from removing the risks listed above?
What having enough sleep gives you
The research results show that, adequate sleep will help you in the following ways:
# You will have more energy (and be more productive);
# You control your weight better;
# It makes you more creative;
# It makes you more emotionally intelligent and able to pick up vital, subtle, non-verbal and verbal cues from people in interpersonal communication; and:
# It makes you look younger!
Some ‘killer facts’ mentioned in the book
 In addition to these benefits, Walker mentions two other important facts. The first concerns sleep, and the other learning and memory (of particular interest to students).
In addition to these benefits, Walker mentions two other important facts. The first concerns sleep, and the other learning and memory (of particular interest to students).
Firstly, it has been discovered that a single night of inadequate sleep (of just 4 hours) destroys 70% of the ‘natural killer cells’ in the immune system! Those killer cells are what protects us from various pathogenic invaders of our bodies.
Secondly, if you are a student trying to learn new information, Matthew Walker has some great advice for you:
On his ‘You Tube’ talk entitled ‘Why We Sleep’, he shows the power of sleep in relation to learning and memory:
~~~
What All-nighters do to your learning efficiency
As described in the video clip above, Walker did some research on sleep and learning. One of the things he investigated was this: If we go to an all-night party (or cram for an exam all night), and have no sleep, would it affect our ability to learn the following day? Dr Walker wanted to test the hypothesis (a testable statement), that “Pulling an all-nighter is a good idea”, so he set up a research experiment:
Two groups of healthy young adults were split into a ‘Sleep’ group and a ‘Sleep Deprivation’ group. The ‘Sleep’ group were going to get a full eight hours’ sleep, and the ‘Deprivation’ group were going to keep awake all night, under supervision, with no caffeine or naps.
Then the following day, the members of each group were placed in an MRI scanner – (which can monitor their brain functioning) – and were asked to learn a whole list of new facts, as snapshots were taken of their brains’ activities. Following that, the participants were all tested to see how effective the learning had been.
When the learning efficiency of the two groups was compared, there was an amazing 40% difference in the ability of the brain to make new memories as between the two groups. So all-nighters have to pay a mental price tag in terms of almost halving their ability to learn!
If you are a student, or learning new material of any kind, then this has to be ‘a wakeup call’ for you (if you will pardon the paradoxical pun!).
Matthew Walker made the following statement in response to these findings, about the impact of sleep on our ability to learn new information:
“This should be frightening considering what we know in our education populations right now about what is happening to sleep. It would be the difference between ‘aceing’ an exam and failing it miserably”
He goes on to say:
“It’s been recently discovered that you need sleep before learning, to prepare your brain, so it’s almost like a dry sponge, ready to soak up new information.
Sleep after learning is essential to hit the ‘SAVE’ button on those new memories so you don’t forget them”.
He then also goes on to state that:
“Without sleep our memory circuits effectively become waterlogged and you can’t absorb information.”
So, to be clear, we need adequate sleep to prepare to soak up new information; and we need adequate sleep afterwards to consolidate the learning (in the form of memory traces in the brain).
Conclusion
This evidence about the importance of sleep has emerged over the last 20 years, and has massive implications for our health, and our ability to learn, to interact with others effectively, and to enjoy life.
Since I read the review by James McConnachie, I have been religiously making sure I get at least 8 hours’ sleep per night, and intend to get Matthew Walker’s book. I strongly recommend it, and also watching him talking on ‘You Tube.’
But please bear in mind: This blog has given you some of the latest information about sleep from an expert. I’ve just given you some declarative knowledge (which means that you’ve now got some information that can be retained or stored; or articulated or stated to another person). This has to be distinguished from what we call ‘procedural knowledge’. That is to say, knowing how to tie shoe laces is not at all the same thing as being able to tie shoe laces.
If you want this information about sleep to improve your quality of life – your health and relationships, your learning and memorizing ability, and safety when driving – then you need to turn this information into procedural knowledge.
You need to actively change your sleep patterns, which are most likely well established habits!
You need to be able to stick to your commitment to change your sleep habits, and assertively alter them in the face of possible pressure from others. As Dr Phil said, “This is when the rubber hits the road”.
 If you want support in doing this, that’s when coaching can be a great moral and practical support. So contact me if you want to take on board these findings and change your sleep patterns for the better.
If you want support in doing this, that’s when coaching can be a great moral and practical support. So contact me if you want to take on board these findings and change your sleep patterns for the better.
That’s all for now.
Best wishes,
Renata
Renata Taylor-Byrne
Lifestyle Coach-Counsellor
The Coaching/Counselling Division
Email: renata@abc-counselling.org
Telephone: 01422 843 629
~~~
Sleep,



 According to a new research report, listening to Mozart and Johann Strauss’s music can help lower hypertension, which means really high blood pressure. Listening to Mozart can not only soothe your mood, but also help lower blood pressure as well as stabilise the heart rate.
According to a new research report, listening to Mozart and Johann Strauss’s music can help lower hypertension, which means really high blood pressure. Listening to Mozart can not only soothe your mood, but also help lower blood pressure as well as stabilise the heart rate. A fortnight ago I heard an amazing sound on Zoe Ball’s BBC Radio 2 music programme, and I enjoyed listening to it so much that this is one of my daily balloons, as it is full of energy and movement.
A fortnight ago I heard an amazing sound on Zoe Ball’s BBC Radio 2 music programme, and I enjoyed listening to it so much that this is one of my daily balloons, as it is full of energy and movement.
 But we did not make up these materialistic beliefs ourselves. All the relentless advertising messages, and propaganda from the media, create this illusion: Having new possessions will really make life better for us, and guarantee our happiness.
But we did not make up these materialistic beliefs ourselves. All the relentless advertising messages, and propaganda from the media, create this illusion: Having new possessions will really make life better for us, and guarantee our happiness.
 Seventy-five years ago, ‘The Harvard Study of Adult development’ was established. A group of researchers started studying 724 teenagers through to their old age. The participants were from two very different types of backgrounds:
Seventy-five years ago, ‘The Harvard Study of Adult development’ was established. A group of researchers started studying 724 teenagers through to their old age. The participants were from two very different types of backgrounds: Here’s what Robert Waldinger states:
Here’s what Robert Waldinger states: He then states: “And living in the midst of good, warm relationships is protective.”
He then states: “And living in the midst of good, warm relationships is protective.” It might seem that physical pain is physical pain, and that is that. But we have always known that physical pain and emotional pain are mediated through the same nerve networks. Here Waldinger explains how pain can be experienced in different ways:
It might seem that physical pain is physical pain, and that is that. But we have always known that physical pain and emotional pain are mediated through the same nerve networks. Here Waldinger explains how pain can be experienced in different ways: Although maintaining the quality of our relationships is the key to health and happiness, there ain’t no quick fixes. You have to work at building relationships! You cannot buy them ready made!
Although maintaining the quality of our relationships is the key to health and happiness, there ain’t no quick fixes. You have to work at building relationships! You cannot buy them ready made! Well, my research shows that most people do not know how to listen effectively. They most often engage in interruptions of the speakers concerns. Perhaps I should give you some examples of those kinds of ‘roadblock’ to communication.
Well, my research shows that most people do not know how to listen effectively. They most often engage in interruptions of the speakers concerns. Perhaps I should give you some examples of those kinds of ‘roadblock’ to communication. The first four responses are judging responses; the second four are ways in which people send solutions to you; and the final three responses are ways in which the ‘listener’ is avoiding your concerns.
The first four responses are judging responses; the second four are ways in which people send solutions to you; and the final three responses are ways in which the ‘listener’ is avoiding your concerns.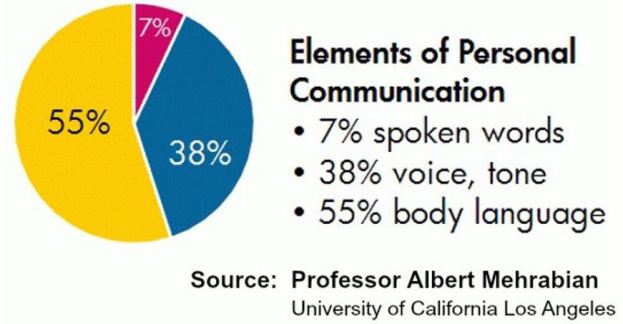
 Jenny Rogers is an executive coach with more than 25 years’ experience, and her clients are usually senior leaders from a wide range of organisations. She has also trained many hundreds of coaches and managers in coaching skills.
Jenny Rogers is an executive coach with more than 25 years’ experience, and her clients are usually senior leaders from a wide range of organisations. She has also trained many hundreds of coaches and managers in coaching skills. Julie Starr, a highly respected coach and consultant, wrote the book ‘The Coaching manual’, which was one of the set books on my Coaching Diploma course! In it she states that:
Julie Starr, a highly respected coach and consultant, wrote the book ‘The Coaching manual’, which was one of the set books on my Coaching Diploma course! In it she states that: People love to be distracted! Makeovers, new clothes, new cars or houses, holidays and other material goods or experiences can be very pleasurable distractions in the short term. But there is one big drawback which you’ll never hear about from the media. Here it is:
People love to be distracted! Makeovers, new clothes, new cars or houses, holidays and other material goods or experiences can be very pleasurable distractions in the short term. But there is one big drawback which you’ll never hear about from the media. Here it is: I have had the privilege for years of seeing the happiness and sense of achievement shine out of clients’ faces when they achieve their goals. For example, I have helped many students to achieve their academic qualifications, at the end of a course which has been a tough battle for them; but they made it through! I was so proud of them, and they wisely took pictures at their presentation events so they could treasure the event for the rest of their lives and show them to their families.
I have had the privilege for years of seeing the happiness and sense of achievement shine out of clients’ faces when they achieve their goals. For example, I have helped many students to achieve their academic qualifications, at the end of a course which has been a tough battle for them; but they made it through! I was so proud of them, and they wisely took pictures at their presentation events so they could treasure the event for the rest of their lives and show them to their families.
 So how, in such a demanding environment, do we manage our energy successfully? So that we optimise our productivity, but conserve our energy and protect our physical and mental health.
So how, in such a demanding environment, do we manage our energy successfully? So that we optimise our productivity, but conserve our energy and protect our physical and mental health. Each day, at the end of the final teaching session, I would wipe the whiteboard clean of all the information that was on it, and I would remember all the outstanding events of the day, good and bad, and wipe them away in my mind at the same time.
Each day, at the end of the final teaching session, I would wipe the whiteboard clean of all the information that was on it, and I would remember all the outstanding events of the day, good and bad, and wipe them away in my mind at the same time. The other aspect of this approach was this: I was asserting my boundaries with my job. In other words, I was taking responsibility for managing upwards. I was not allowing myself to develop ‘leaky boundaries’ through which outside forces could use up my precious reserves of energy!
The other aspect of this approach was this: I was asserting my boundaries with my job. In other words, I was taking responsibility for managing upwards. I was not allowing myself to develop ‘leaky boundaries’ through which outside forces could use up my precious reserves of energy! Some years ago I found this idea was used by Olympic athletes. After they had been working on the skills they wanted to develop, then they needed time to rest and recover. The human body needs proper recovery for sustained and improved performance, for development, and even for preventing injuries.
Some years ago I found this idea was used by Olympic athletes. After they had been working on the skills they wanted to develop, then they needed time to rest and recover. The human body needs proper recovery for sustained and improved performance, for development, and even for preventing injuries.



 In this blog I am going to do a ‘rave review’ of a short and simple quiz that shows us how we handle conflict in our current relationships. Some quizzes don’t give us many insights about ourselves when we’re interacting with other people, but this one strikes me as giving us a clear mirror which shows us how we deal with pressure from others.
In this blog I am going to do a ‘rave review’ of a short and simple quiz that shows us how we handle conflict in our current relationships. Some quizzes don’t give us many insights about ourselves when we’re interacting with other people, but this one strikes me as giving us a clear mirror which shows us how we deal with pressure from others.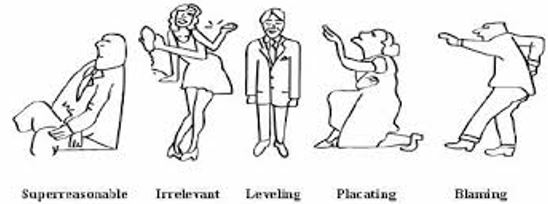
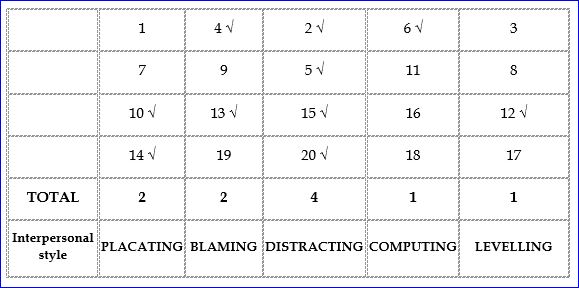
 Virginia Satir’s conflict categories:
Virginia Satir’s conflict categories: Levelling
Levelling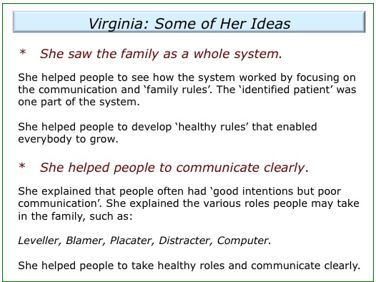
 Learning new behaviours
Learning new behaviours In this blog I am going to summarise some findings from research conducted on athletes, which can help us build our resilience in the face of all the hassles and challenges we can face at work each day.
In this blog I am going to summarise some findings from research conducted on athletes, which can help us build our resilience in the face of all the hassles and challenges we can face at work each day. Bonnie St. John and Allen Haines wrote a book called ‘Micro-resilience’, and in it they summarise this research finding: Dr James Loehr (a sports psychologist) wanted to understand why there were hundreds of athletes who were on international tours, but there were only a few who regularly won the tournaments and trophies. He wanted to know what the difference was between these two sets of athletes.
Bonnie St. John and Allen Haines wrote a book called ‘Micro-resilience’, and in it they summarise this research finding: Dr James Loehr (a sports psychologist) wanted to understand why there were hundreds of athletes who were on international tours, but there were only a few who regularly won the tournaments and trophies. He wanted to know what the difference was between these two sets of athletes. Dr James Loehr created the concept of the ‘executive athlete’ after these research findings, which he wrote about in his book ‘The Power of Full Engagement’ (2003) with T. Schwartz.
Dr James Loehr created the concept of the ‘executive athlete’ after these research findings, which he wrote about in his book ‘The Power of Full Engagement’ (2003) with T. Schwartz. First, let us look at the ‘death pose’ from yoga practice. This is an amazingly effective way to recharge your batteries, and is very good for your back. If you have you own office or there is a vacant room, simply lie on the floor for 10 minutes with a book (of, say, two inches thickness) under your head (as a ‘hard pillow’). Put your arms down by your sides. Clear your mind of any stress or strain, worry or preoccupation. Breathe deeply into your belly, and relax. Stay still, and close your eyes if you want to. Any ideas that arise in your mind should be gently brushed away. After 10 minutes, very slowly sit up, and then stand up. This will refresh your body and mind at the same time.
First, let us look at the ‘death pose’ from yoga practice. This is an amazingly effective way to recharge your batteries, and is very good for your back. If you have you own office or there is a vacant room, simply lie on the floor for 10 minutes with a book (of, say, two inches thickness) under your head (as a ‘hard pillow’). Put your arms down by your sides. Clear your mind of any stress or strain, worry or preoccupation. Breathe deeply into your belly, and relax. Stay still, and close your eyes if you want to. Any ideas that arise in your mind should be gently brushed away. After 10 minutes, very slowly sit up, and then stand up. This will refresh your body and mind at the same time.


 I like lists, and I thought you might like to see this list I have created about the value of having a coach. Some people may well feel that they are not entitled to have a coach. I don’t think Rihanna, Britney Spears, Gwen Stefani, Serena Williams or Andy Murray would agree with them.
I like lists, and I thought you might like to see this list I have created about the value of having a coach. Some people may well feel that they are not entitled to have a coach. I don’t think Rihanna, Britney Spears, Gwen Stefani, Serena Williams or Andy Murray would agree with them. That’s all for this week.
That’s all for this week.